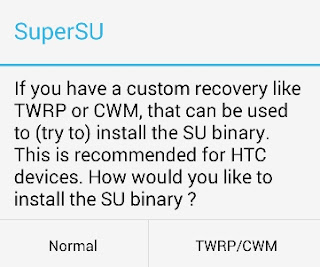
REVERSING AND BYPASSING AUTHENTICATION WITH D2J-DEX2JAR AND JD-GUI
- Layout for this exercise:
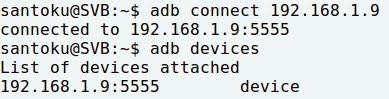
- Connecting Santoku to Nexus 5:
1 - D2J-DEX2JAR
- dex2jar decompiles the Dalvik bytecode (dex) into readable Java source. The resulting source is useful to read and understand the functionality of an app. However, it is important to notice that the code cannot be modified and repackaged with dex2jar.
2 - JAVA DECOMPILER - JD GUI
- The Java Decompiler project (JD) aims to develop tools in order to decompile and analyze Java 5 byte code and the later versions.
- JD-Core is a library that reconstructs Java source code from one or more .class files. JD-Core may be used to recover lost source code and explore the source of Java runtime libraries. New features of Java 5, such as annotations, generics or type “enum”, are supported. JD-GUI and JD-Eclipse include JD-Core library.
- JD-GUI is a standalone graphical utility that displays Java source codes of .class files. The reconstructed source code can be browsed with the JD-GUI for instant access to methods and fields.
- JD-Eclipse is a plug-in for the Eclipse platform. It allows to display all the Java sources during the debugging process, even if not having them all.
- JD-Core, JD-GUI & JD-Eclipse are open source projects released under the GPLv3 License.
3 - BYPASSING AUTHENTICATION OF THE APPLICATION LISTLOCK
- To illustrate the usage of d2j-dex2jar and jd-gui the application ListLock is downloaded from this link:
- Once downloaded all the content, let's unzip:
- Going to the ListLock APK folder, there is the .apk file com.gdssecurity.listlock.apk:
- Installing the application to the mobile device:
- Clicking the icon:
- The user is prompted to enter a password. Using a bad password, the list keeps on being locked:
- Let's reverse the application with d2j-dex2jar:
- A new .jar file is created:
- Opening the .jar file with jd-gui:
- Going to the classes, there is an Authenticate.class that includes the method validatePassword. This method compares the saved password (PasswordStore.class) and the password entered by the user. In case of matching (equals) the list is unlocked:
- However, PasswordStore.class hardcodes the password to be compared, what is a common vulnerability in many applications:
- Using the hardcoded password (C@ntSeeMyList!) the list is successfully unlocked: